SNMP, which stands for Simple Network Management Protocol, is a network protocol used to manage and monitor network devices such as routers, switches, servers, printers, and more. It allows network administrators to collect information about these devices, monitor their performance, and manage them remotely. SNMP operates in a client-server model, where SNMP agents on network devices collect and store information, and SNMP managers retrieve and process this information to monitor and manage the network.
The SNMP protocols 1, 2, and 2c don’t encrypt network traffic, so anyone on the same network can see SNMP data and passwords. SNMPv3 only supported a weak encryption method called DES-56, which can be easily cracked. A newer version of SNMPv3 now supports a stronger encryption method called AES-256.
SNMP MIB
The SNMP Management Information Base (MIB) is like a tree-formatted database used for network management. Each branch of the tree represents different aspects of a network, like devices or functions. The “leaves” of the tree hold specific information, such as variable values, that can be accessed and managed by users. The IBM Knowledge Center is a good resource for learning more about this structure.
SNMP MIB Values Table:
1.3.6.1.2.1.25.1.6.0 – System Processes
1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.2 – Running Programs
1.3.6.1.2.1.25.4.2.1.4 – Processes Path
1.3.6.1.2.1.25.2.3.1.4 – Storage Units
1.3.6.1.2.1.25.6.3.1.2 – Software Name
1.3.6.1.4.1.77.1.2.25 – User Accounts
1.3.6.1.2.1.6.13.1.3 – TCP Local Ports
Enumeration
Enumerate hosts to find which are running SNMP:sudo nmap -sU --open -p161 <TARGET_IP_ADDRESS> -oG <OUTPUT_FILE_GREPPABLE>

Bruteforcing SNMP Community
OneSixtyOne is used to brute force SNMP community string.onesixtyone -c <COMMUNITY_LIST_FILE> -i <TARGET_IP_LIST_FILE>

SNMPwalk
Using SNMPwalk to find more information about the target server using the discovered community string (public).snmpwalk -c public -v1 <TARGET_IP_ADDRESS> <SNMP_MIB_VALUE>


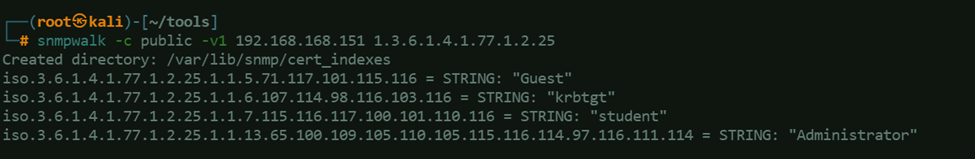
snmpwalk -c public -v1 -t 10 <TARGET_IP_ADDRESS> -Oa
-Oa parameter in the command automatically translates any hexadecimal string into ASCII that was not decoded previously. This can be really helpful when dealing with encoded or encrypted data, as it simplifies the process of understanding the data gathered using SNMP.